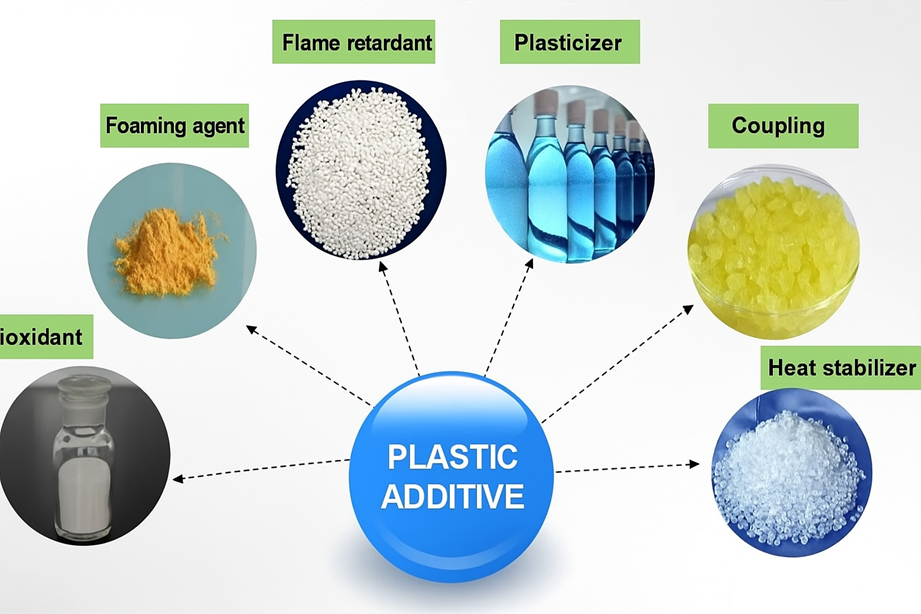
Different types of additives are often added during the processing of plastics to meet the different processing and application requirements of the materials, and the selection of additives is crucial in the design of plastic modification formulations.
I. Definition of plastic additives
Plastic additives, also known as plastic auxiliaries, are compounds that must be added to polymers (synthetic resins) during molding and processing to improve their processing performance or to compensate for deficiencies in the resin’s own properties.
1. Plasticizers can be added to lower the molding temperature of polyvinyl chloride resin and make the product softer;
2. Foaming agents can be added to prepare lightweight, vibration-resistant, heat-insulating, and sound-insulating foamed plastics;
3. Some plastics have thermal decomposition temperatures that are very close to their molding and processing temperatures, and cannot be molded without the addition of heat stabilizers.
Therefore, plastic additives occupy a particularly important position in plastic molding and processing.
II . Basic Requirements and Application Precautions for Selecting Additives
1. Additives should have good compatibility with plastics so that they can exist stably and uniformly in the product for a long time and exert their effectiveness. If the compatibility is poor, the additives are prone to precipitation.
2. Additives should be durable. Choose additives that do not easily migrate from the plastic.
3. The additives should have good adaptability to processing conditions. They should not easily decompose or volatilize at processing temperatures.
4. Additives must not be harmful or toxic to the product and must meet hygiene standards.
III . Selection Methods for Plastic Additives
1. Select adjuvants according to their purpose
Improve processing performance : Lubricants, release agents, stabilizers, processing aids, thixotropic agents, plasticizers, PVC stabilizers.
Improve mechanical properties : plasticizers, reinforcing fillers, toughening agents, and impact modifiers.
Improving optical properties : Pigments, dyes, nucleating agents, and fluorescent whitening agents.
Improved aging performance : antioxidants, PVC stabilizers, UV absorbers, bactericides, and mildew inhibitors.
Improve surface properties : antistatic agents, lubricants, abrasion resistant agents, anti-blocking agents, anti-fogging agents.
Cost reduction : diluents, fillers.
Improve other properties : foaming agent, combustion aid, chemical crosslinking agent, coupling agent, etc.
2. The additives are selective for the resin.
Red phosphorus flame retardants are effective for PA, PBT, and PET; nitrogen-based flame retardants are effective for oxygen-containing plastics, such as PA, PBT, and PET; heat-resistant modification of glass fiber is effective for crystalline plastics but poor for amorphous plastics; carbon black fillers are effective in crystalline resins; nucleating agents are effective for copolymer polypropylene.
3. Compatibility between additives and resin
The additives and resins must have good compatibility to ensure that they are dispersed according to the intended structure, thus guaranteeing the achievement of design specifications and ensuring that their effects are sustained throughout their service life, with resistance to extraction, migration, and precipitation.
Apart from a few additives such as surfactants, good compatibility with resin is the key to maximizing their effectiveness and increasing their dosage.
Therefore, it is necessary to find ways to improve or enhance its compatibility, such as by using compatibilizers or coupling agents for surface activation treatment.
4. Selection of the shape of the additive
Fibrous additives have a good reinforcing effect. The degree of fiberization of the additive can be expressed by the aspect ratio. The larger the aspect ratio, the better the reinforcing effect. This is why we add glass fiber through the venting holes.
Molten state is more conducive to maintaining aspect ratio and reducing the chance of fiber breakage than powder. Spherical additives have better toughening effect and higher gloss.
Barium sulfate is a typical spherical additive, so it is used as a filler for high-gloss PP, and can also be used for minor rigidity and toughening.
5. Amount of additives added
The appropriate amount of additives can not only improve the target resin to a suitable performance, but also keep costs low based on economic principles.
Different additives require different dosage requirements:
1) Flame retardants, toughening agents, magnetic powders, barrier agents, etc., although the more they are added, the better from a performance perspective, but the cost must also be determined;
2) Conductive additives, generally only need to form a circuit path;
3) Antistatic agent, simply form a charge-dissipating layer on the surface;
4) Coupling agent, which can be used to form a surface coating.
Post time: Nov-06-2025