The material's " close protection " ---UV531
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation—this invisible "light assassin"—constantly threatens the lifespan and stability of various materials. As an "optical shield" against UV radiation, UV absorbers have become indispensable guardians of modern industry. To understand their remarkable effects, we first need to recognize the true nature of this "invisible killer."
In the hidden corners of the solar spectrum (100-400nm), ultraviolet radiation lurks three dangerous special forces:
|
Classification |
Wavelength range (nm) |
Features |
|
UV-A |
320-400 |
Long-wave ultraviolet light has strong penetrating power and can penetrate clouds and glass. |
|
UV-B |
280-320 |
Medium-wave ultraviolet radiation is partially absorbed by the ozone layer and has weak penetrating power. |
|
UV-C |
100-280 |
Short-wave ultraviolet radiation is almost completely absorbed by the ozone layer, and little of it remains on the Earth's surface. |
- UV-C Special Forces : Carrying the most lethal high-energy rays, fortunately the ozone layer forms the first line of defense for the Earth, making it very rare for them to reach the ground.
- UV-B Vanguard : Specializing in targeting material surfaces, it can trigger molecular chain breakage reactions, making it a major culprit for plastic embrittlement and paint fading.
- UV -A Penetrating Agent : A 'lurker' with super penetrating power, capable of penetrating deep into the interior of materials to trigger a slow but continuous degradation process. Targeting the characteristics of these enemies in different wavelengths, ultraviolet absorbers have developed ingenious defensive tactics—through special functional groups in their molecular structure, they convert the destructive energy of ultraviolet rays into harmless heat, providing tailor-made optical protective clothing for materials such as plastics, coatings, and cosmetics.
I. Classification of Ultraviolet Absorbers
In modern industry and daily life, the aging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on materials cannot be ignored. To address this challenge, scientists have developed a variety of UV absorbers, which are light stabilizers that absorb the ultraviolet rays from sunlight and fluorescent light sources without changing their own properties. Based on their chemical structures, UV absorbers are mainly classified into benzotriazoles, triazines, and benzophenones (such as UV531).
When selecting ultraviolet absorbers, special attention should be paid to the absorption coefficient of different resins to ultraviolet light in order to select the appropriate ultraviolet light to form the "most suitable" protection for the resin.
1. PVC: The absorption coefficient is low at short wavelengths (200-300 nm), but it increases significantly with increasing wavelength, indicating that PVC is more sensitive to long-wave ultraviolet light.
2. PE: The low absorption coefficient indicates that PE has a weak ability to absorb ultraviolet light and good resistance to ultraviolet light.
3. PS: The absorption coefficient is moderate, especially the absorption is strong in the 300-400 nm range.
4. PC: It has a high absorption coefficient, especially in the long-wave ultraviolet range (350-400 nm), where it exhibits strong absorption capacity.
5. PET: It has a high absorption coefficient, especially in the 300-400 nm range where absorption is significant.
6. EPOXY: It has the highest absorption coefficient, indicating that EPOXY is very sensitive to ultraviolet light and is prone to aging.
II. Introduction to UV531 - A classic benzophenone-based ultraviolet absorber
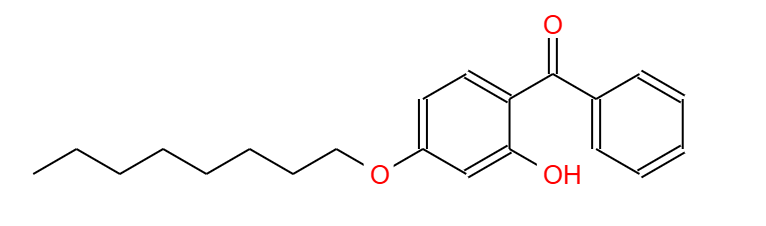
Structural formula:
Reaction mechanism: UV531 is a typical benzophenone-based ultraviolet absorber. The absorption mechanism of UV-531 (2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxybenzophenone) is mainly based on the response of specific chemical bonds in its molecular structure to ultraviolet light.
The specific process is as follows:
1. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding and chelate ring formation
The carbonyl and hydroxyl groups in the UV-531 molecule can form intramolecular hydrogen bonds, creating a chelate ring. This structure gives it a specific electron cloud distribution, providing a basis for absorbing ultraviolet light.
2. Ultraviolet energy absorption
When a molecule is exposed to ultraviolet light of a specific wavelength, it absorbs energy and enters an excited state. At this point, the molecular thermal vibrations intensify, leading to the breaking of intramolecular hydrogen bonds and the opening of chelate rings.
3. Energy Conversion and Release
The ring-opening process converts the high energy of ultraviolet light into heat or other low-energy forms (such as vibrational energy), thus preventing the polymer from absorbing ultraviolet energy and inducing photooxidation. Subsequently, the molecule returns to its initial structure and can repeatedly absorb ultraviolet light.
4. Photostability and Cycling Effect
UV-531 itself has high photostability and can theoretically absorb and release ultraviolet energy indefinitely. However, in practical applications, its performance may gradually deteriorate due to long-term exposure to environments such as peroxide free radicals. Therefore, it is often used in combination with other light stabilizers (such as hindered amine light stabilizers) to enhance the protective effect.
III. Unique Advantages of UV531 - A Guardian of Highly Effective Anti-Aging
1. Highly efficient absorption of the UV-B band: UV531 is designed to absorb the UV-B band (280-320 nm).
This is the main UV band that causes material aging and sunburn. UV531 has higher absorption efficiency in the UV-B band, making it particularly suitable for scenarios requiring strong protection.
2. Excellent light and thermal stability
UV531 maintains a stable chemical structure even under prolonged exposure to light and high temperatures, making it resistant to decomposition and ensuring long-lasting protection.
3. Broad compatibility
UV531 exhibits good compatibility with various polymer materials (such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride), making it easy to process and apply.
4. Environmental protection and safety
UV531 has undergone rigorous toxicological testing and is harmless to humans and the environment, meeting international environmental standards and is safe for use in food packaging and cosmetics. In contrast, benzotriazoles and triazines may pose certain environmental risks due to the presence of halogens or other harmful components. For example, four phenolic benzotriazole substances (including UV-328, UV-327, UV-350, and UV-320) have been proposed for REACH restrictions by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA).
IV. Application Areas of 531 - Wide Coverage of Various Materials
UV-531, as a high-performance and highly effective anti-aging additive, has a wide range of applications. The following are the main application areas of UV-531:
- Plastics industry

UV-531 has significant application value in the plastics industry. It effectively absorbs ultraviolet light, reducing aging caused by UV exposure and thus extending the lifespan of plastics. Specifically, UV-531 is widely used in the following plastic materials:
- Polyethylene (PE): Whether it's high-density polyethylene or low-density polyethylene, UV-531 provides effective light stabilization. It is particularly effective in agricultural films, significantly extending their lifespan.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): PVC materials are prone to yellowing and changes in physical properties under ultraviolet radiation. The addition of UV-531 can effectively alleviate these problems and improve the weather resistance of PVC materials.
- Polypropylene (PP): UV-531 provides excellent anti-aging properties in both colored and colorless polypropylene. Its dosage typically increases as the thickness of the finished product decreases.
- Polystyrene (PS) and polycarbonate (PC): UV-531 is also suitable for these plastic materials, providing them with good light stabilization.
2. Rubber Industry
In rubber products, UV-531 also provides excellent anti-aging protection. It can improve the weather resistance and durability of rubber products, extending their service life.

3. Coatings industry
UV-531 also has wide applications in the coatings industry. It is suitable for various coatings, such as drying phenolic and alkyd varnishes, polyurethanes, acrylics, and epoxys. The addition of UV-531 can provide these coatings with good light stability, making the coating more durable.

4.Other application areas
In addition, UV-531 can be used in products such as ethylene vinyl acetate, powder coatings, and automotive finishing paints, providing them with excellent light stabilization. Furthermore, UV-531 can be used in combination with light stabilizers and antioxidants to further improve anti-aging and anti-yellowing properties.
In summary, UV-531 has a wide range of applications, covering multiple industries such as plastics, rubber, coatings, fibers, and personal care products. Its excellent anti-aging properties and broad application prospects make UV-531 play an increasingly important role in industrial production and daily life.
Post time: Nov-28-2025